The Transistor is used as a amplifying element which is used to amplify the given signal. The amplifier is the semiconductor device and which contain 3 terminals for connection to external circuits. Materials most commonly used are silicon, gallium-arsenide, and germanium, into which impurities have been introduced by a process called “doping.”
There are three main classifications of transistors each with its own symbols, characteristics, design parameters,
and applications. See below and the following pages for additional details and applications on each of these
transistor types. Several special-function transistor types also exist which do not fall into the categories below,
such as the unijunction (UJT) transistor that is used for SCR firing and time delay applications. These specialfunction
devices are described separately.
1. Bipolar transistors are considered current driven devices and have a relatively low input impedance. They
are available as NPN or PNP types. The designation describes the polarity of the semiconductor material
used to fabricate the transistor.
2. Field Effect Transistors, FET’s, are referred to as voltage driven devices which have a high input impedance.
Field Effect Transistors are further subdivided into two classifications: 1) Junction Field Effect Transistors,
or JFET’s, and 2) Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors or MOSFET’s.
3. Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors, known as IGBT’s, are the most recent transistor development. This hybrid device combines characteristics of both the Bipolar Transistor with the capacitive coupled, high impedance
input, of the MOS device
The Transistor is the fundamental block of the electronic devices and most of the electronic systems. A transistor may be used as a switch and as an amplifier .The amount of current amplification is called the current gain, symbol hFE.
Types of transistor:
There are three main classifications of transistors each with its own symbols, characteristics, design parameters,
and applications. See below and the following pages for additional details and applications on each of these
transistor types. Several special-function transistor types also exist which do not fall into the categories below,
such as the unijunction (UJT) transistor that is used for SCR firing and time delay applications. These specialfunction
devices are described separately.
1. Bipolar transistors are considered current driven devices and have a relatively low input impedance. They
are available as NPN or PNP types. The designation describes the polarity of the semiconductor material
used to fabricate the transistor.
2. Field Effect Transistors, FET’s, are referred to as voltage driven devices which have a high input impedance.
Field Effect Transistors are further subdivided into two classifications: 1) Junction Field Effect Transistors,
or JFET’s, and 2) Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors or MOSFET’s.
3. Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors, known as IGBT’s, are the most recent transistor development. This hybrid device combines characteristics of both the Bipolar Transistor with the capacitive coupled, high impedance
input, of the MOS device
Sunday, January 16, 2011
Resistor and its types
The value of resistance is found by the colour coding only. We can calculate the value by knowing its colour.The colour indicating table is below:
| RESISTOR COLOR CHART | ||||
| Color | 1st Significant Digit | 2nd Significant Digit | Number of zeros (multiplier) | Resistance Tolerance |
| Black | 0 | 0 | 100 | - |
| Brown | 1 | 1 | 101 | 1% |
| Red | 2 | 2 | 102 | 2% |
| Orange | 3 | 3 | 103 | - |
| Yellow | 4 | 4 | 104 | - |
| Green | 5 | 5 | 105 | 0.5% |
| Blue | 6 | 6 | 106 | 0.25% |
| Violet | 7 | 7 | 107 | 0.1% |
| Grey | 8 | 8 | 108 | 0.05% |
| White | 9 | 9 | 109 | - |
| Silver | - | - | 10-2 | 10% |
| GOLD | - | - | 10-1 | 5% |
Types of Resistor:
1) Fixed Resistor
In an electrical circuit, some objects may need a lesser amount of current than the input value. In such cases, fixed resistors are used to reduce the flow of current. They are placed in such a way that a higher voltage must first pass through them before it flows further. The value of the resistance is fixed and does not change with change in the applied voltage or current flowing through it. The resistance value is measured in ohms and the value ranges from a few milliohms to about a giga-ohm.
Working of a fixed resistor:
A fixed resistor has a resisting material in the center and conducting material at the end. Resistance is proportional to the length of the resistor and to the material's resistivity and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. The resistor will be damaged if it is exposed to a voltage greater than its maximum working value. The equation to determine the voltage V through a resistor of resistance R ohms with a current I in amperes is V= IR.
Types of fixed resistors:
Based on the resisting material: carbon and metal oxide film, wire-wound, sand filled.
Based on their power ratings: 1/8, 20 watts, etc.
Resistance value: ranges from a few milliohms to a giga-ohm.
A tolerance of plus or minus 2 to 10% is usually given.
Applications :
Resistors are universally used in all electrical circuits of devices like TVs, radios, refrigerators, machines, microelectronic semiconductor devices, regulators, etc.
Fixed resistors are further classified into
a) Carbon composition type resistors
b) Metalized type resistors
c) Wire wound type resistors
a) Carbon composition type resistors:
This is the most common type of low wattage resistor. The resistive material is of carbon-clay composition and the leads are made of tinned copper. These resistors are cheap and reliable and stability is high.
b)Wire wound resistors:
These resistors are a length of wire wound an insulating cylindrical core. Usually wires of material such as constantan (60% copper and 40% nickel) and manganin which have high resistivities and low temperature coefficients are employed. The completed wire wound resistor is coated with an insulating material such as baked enamel.
c) Metalized resistors
It is constructed using film deposition techniques of depositing a thick film of resistive material onto an insulating substrate.Only approximate values of resistance can be had by this method.
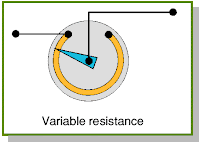
2) Variable Resistance
A variable resistor is a potentiometer with only two connecting wires instead of three. However, although the actual component is the same, it does a very different job. The pot allows us to control the potential passed through a circuit. The variable resistance lets us adjust the resistance between two points in a circuit.
For circuits requiring a resistance that can be adjusted while it remains connected in the circuit ( for eg:volume control on radio), variable resistors are required. They usually have 3 lead two fixed and one movable








No comments:
Post a Comment